
by Douglas Stinson
CRC Press, CRC Press LLC
ISBN: 0849385210 Pub Date: 03/17/95

|
Cryptography: Theory and Practice
by Douglas Stinson CRC Press, CRC Press LLC ISBN: 0849385210 Pub Date: 03/17/95 |
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
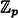 . That is, given t public x-coordinates, x1, x2, . . . , xt, and t y-coordinates y1, . . . , yt, compute the resulting key. Use the Lagrange interpolation method, as it is easier to program.
. That is, given t public x-coordinates, x1, x2, . . . , xt, and t y-coordinates y1, . . . , yt, compute the resulting key. Use the Lagrange interpolation method, as it is easier to program.
shares:
| x1 | = | 413 | y1 | = | 25439 |
| x2 | = | 432 | y2 | = | 14847 |
| x3 | = | 451 | y3 | = | 24780 |
| x4 | = | 470 | y4 | = | 5910 |
| x5 | = | 489 | y5 | = | 12734 |
| x6 | = | 508 | y1 | = | 12492 |
| x7 | = | 527 | y2 | = | 12555 |
| x8 | = | 546 | y3 | = | 128578 |
| x9 | = | 565 | y4 | = | 20806 |
| x10 | = | 584 | y5 | = | 21462 |
Verify that the same key is computed by using several different subsets of five shares.
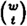 t-subsets of participants, and verifying that the same key is computed in each case. Can you describe a more efficient method of testing the consistency of the shares?
t-subsets of participants, and verifying that the same key is computed in each case. Can you describe a more efficient method of testing the consistency of the shares?| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |